Eclipses 101
While this page mostly focuses on the visual impact of eclipses, those interested in the celestial mechanics of eclipses, see Wikipedia.
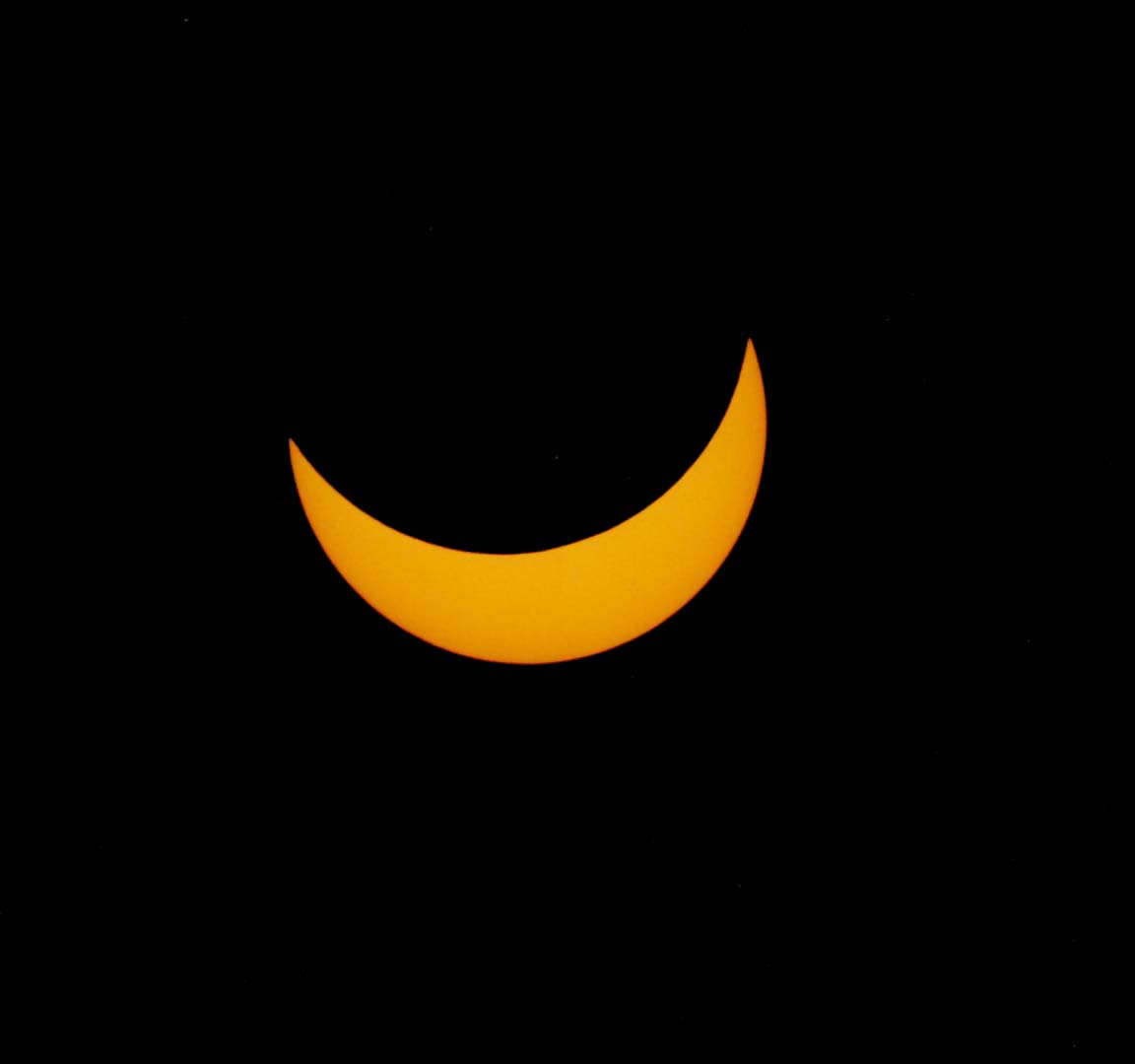
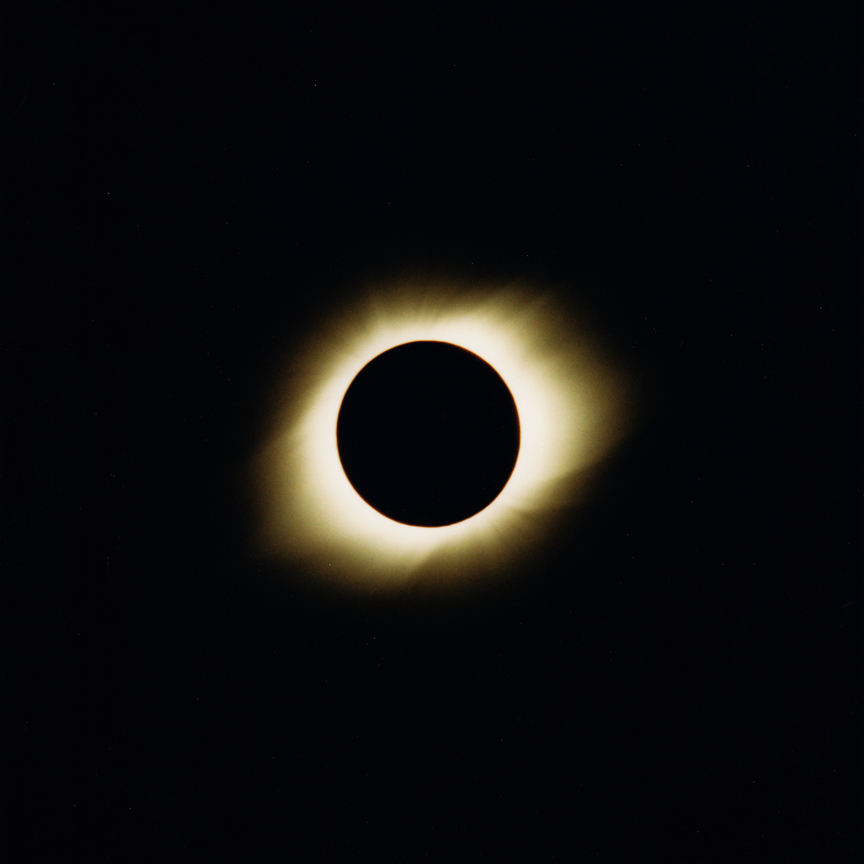
Most people are unaware of the dramatic differences between a partially eclipsed sun — even one that's 99.9% covered by the moon — and a totally eclipsed sun. If you think you've seen a total solar eclipse, then you most certainly never have. Someone not paying attention could easily think the dimming of the sun's light during a partial eclipse might simply be the result of a passing cloud. For an account of one person's first total solar eclipse, as well as more on the differences between partial and total, see http://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2006/clips/clip5.php.
Solar eclipses happen during the day when the moon is new, when the alignment is Sun-Moon-Earth. Partial solar eclipses should never be observed without proper sun filters. Lunar eclipses happen only at night during a full moon, when the alignment is Sun-Earth-Moon.
One of the contributing factors to ignorance of total solar eclipses is how inaccessible they generally are. While both solar and lunar eclipses happen every year or so, the path of totality for solar eclipse is very narrow (around 100 miles wide) and total solar eclipses last anywhere from a fraction of a second to a maximum of seven and a half minutes. Partial solar eclipses can be observed (with proper filters or pinhole projection) over more than a thousand miles and last up to a couple hours or so.
On the other hand, every total lunar eclipse can be observed from a large fraction of the planet at a time. Totality usually lasts about an hour or so, and the partial phases stretch over several hours.
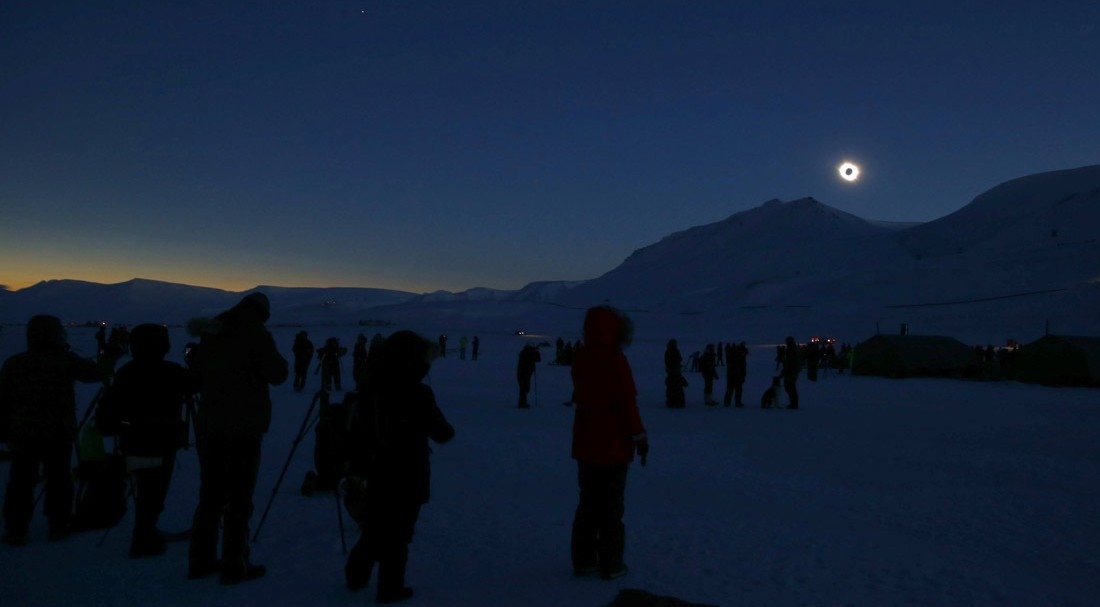
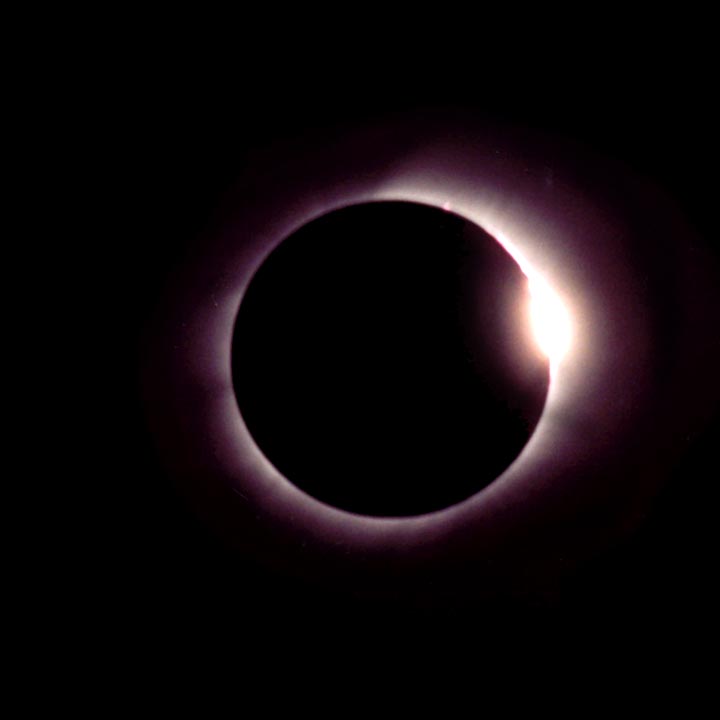
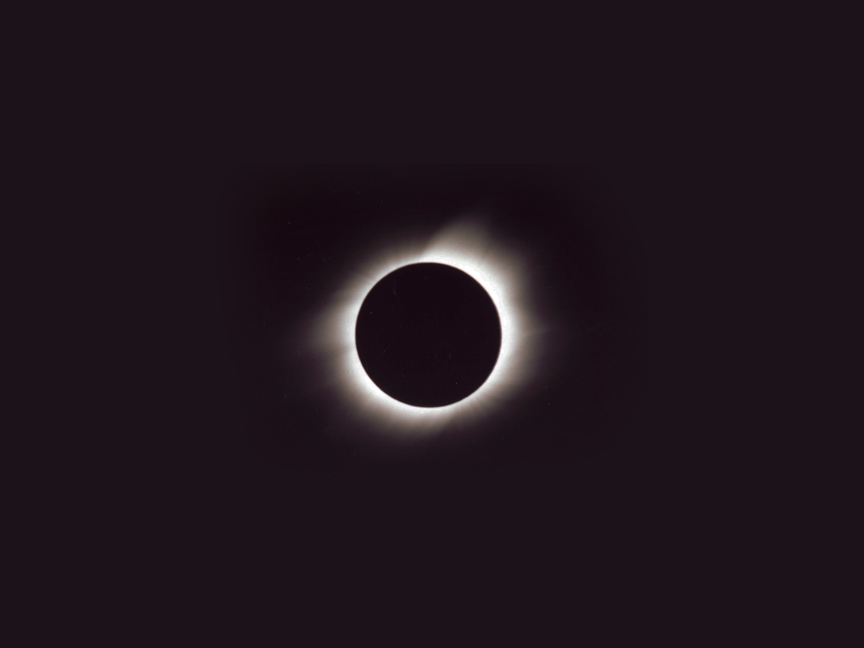
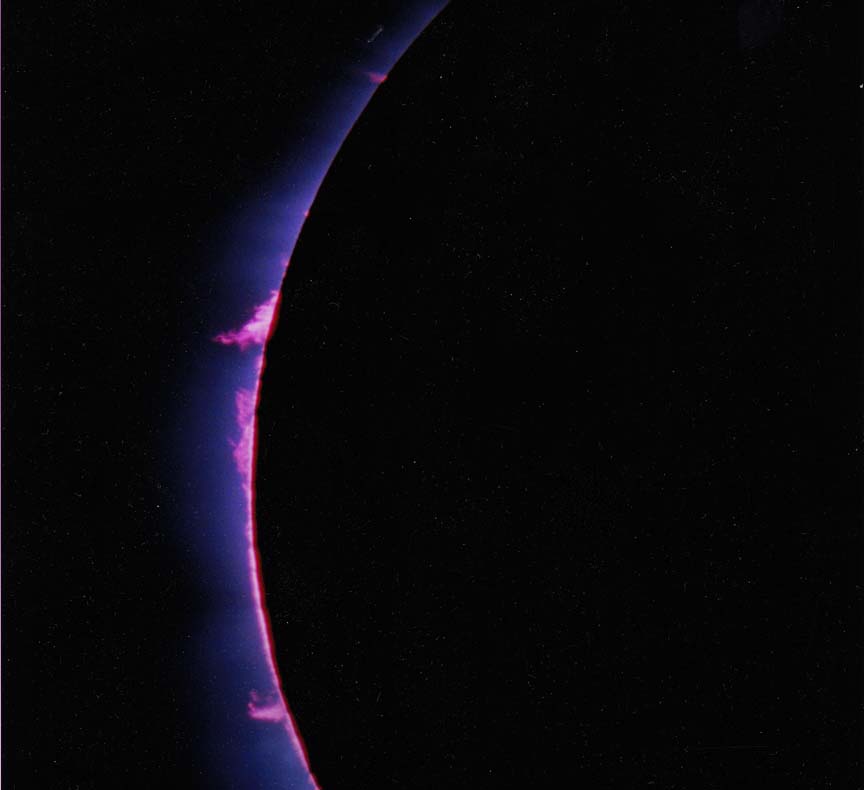
With a total solar eclipse, not only does the sky darken dramatically and the shimmering yellow corona surrounding the black disk of the moon become strikingly visible but other effects (listed below) may appear. Nevertheless even a simple cataloging of effects cannot adequately describe the eerie and unearthly impact it has on observers. Then it's all over in a breathtakingly short time.
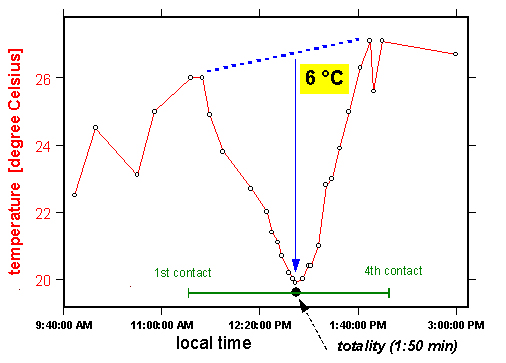
The photos below illustrate how the sun and moon look both normally and during a total eclipse — without the use of filters of any sort. But photos simply cannot do justice to the stunning eerieness of total solar eclipses. There is no substitute for standing in the moon's shadow. Besides the visual — and unlike lunar or partial solar eclipses — total solar eclipses display dramatic changes in temperatures, increase in wind speed, aberrant animal behavior, not to mention human awe.
For the 2016 (9 March) total solar eclipse, one needs to be in or near Indonesia. Totality lasts up to 2 minutes.
However, the 2017 (21 August) total solar eclipse slashes across the United States from Oregon to South Carolina. Totality lasts up to 2 min. 46 sec. There are many websites about the 2017 eclipse, including greatamericaneclipse.com and www.eclipse2017.org.
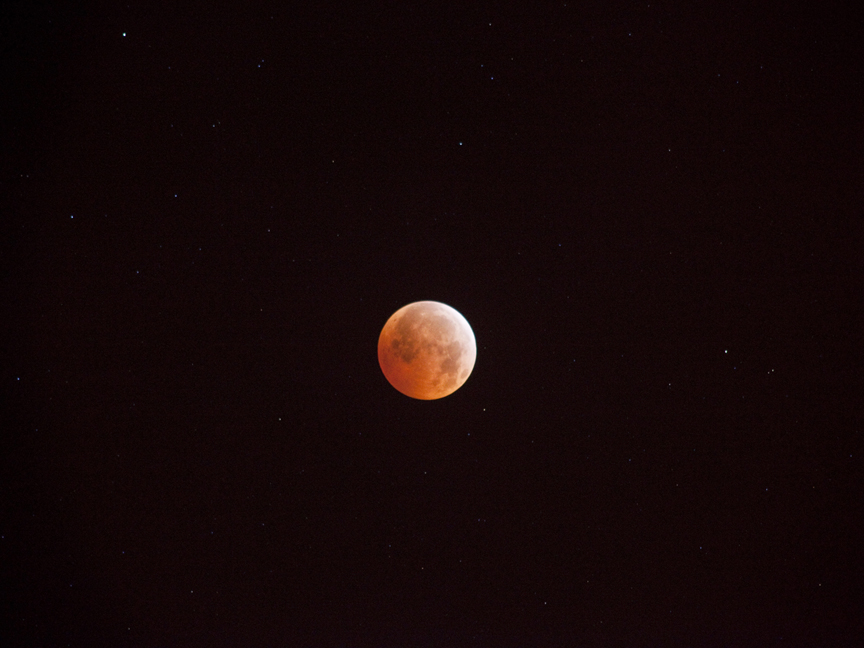
| LUNAR ECLIPSES | |
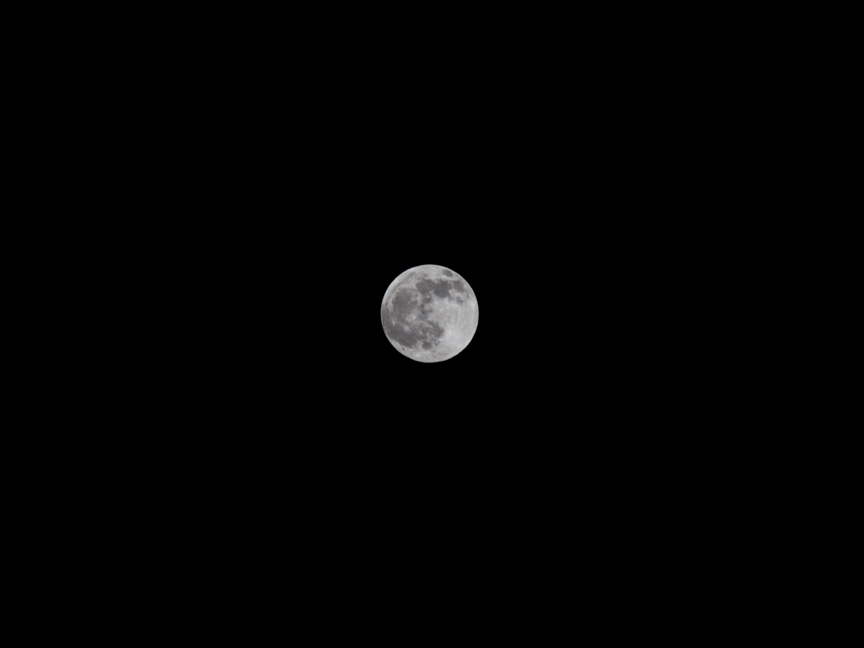
| Naked full moon | Full moon covered by the Earth's shadow |
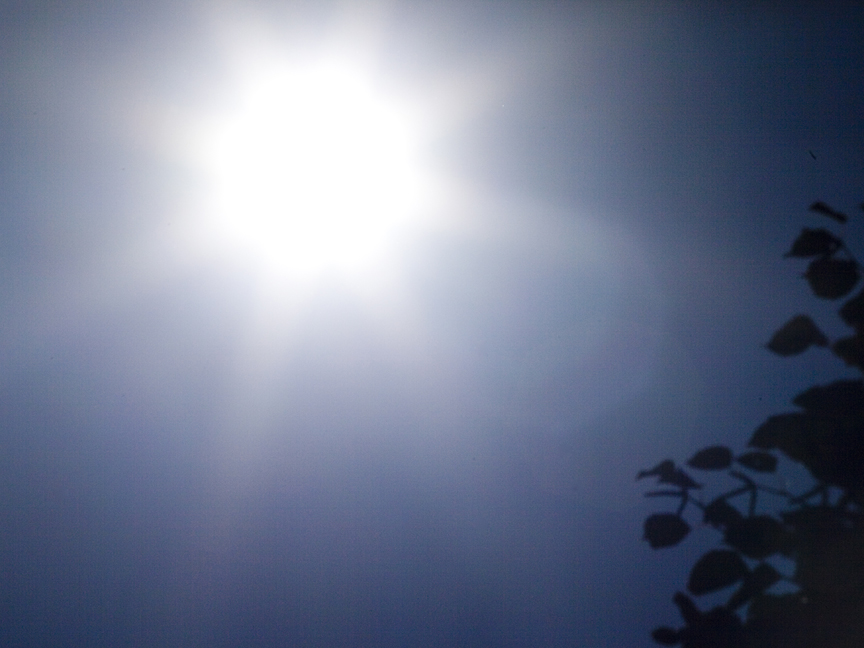
| SOLAR ECLIPSES | |
| Naked sun or even a partially eclipsed sun | Sun totally eclipsed — NOTE: this is a daytime photo |